Self-efficacy Theory: Difference between revisions
Tanvivartak (talk | contribs) m (Tanvivartak moved page Self-efficacy theory to Self-efficacy Theory) |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=='''Overview'''== | =='''Overview'''== | ||
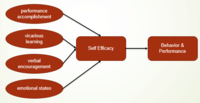
[[File:Self-Efficacy-Bandura-1997.png|200px|thumb|right|Bandura self-efficacy theory]] | [[File:Self-Efficacy-Bandura-1997.png|200px|thumb|right|Bandura self-efficacy theory]] | ||
Psychologist Albert Bandura developed the self-efficacy theory in 1977. In psychology, self-efficacy is the belief that estimates people make about their ability to perform specific actions <ref name="Martinez_motivation">Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ</ref> . People are more likely to perform well in the field they are good at. The experience will gain confidence and lead the person to complete tasks. For example, professional basketball players will feel confident about any basketball-related activity. Still, they will feel less confident about an activity outside their skill pool, such as soccer. In Bandura’s theory, people with high self-efficacy usually believe they can perform well on specific tasks. But people with low self-efficacy are more likely to avoid complex tasks. The difference between high and low self-efficacy people reflects on their mindset on tasks and, more importantly, their understanding of external factors of the task. Based on knowledge of external factors will ultimately affect a person’s motivation to complete challenging tasks. | |||
According to Bandura’s theory, there are four influences on self-efficacy, <b>Performance Accomplishments, Vicarious experience, Verbal persuasion, and Physiological state</b> | According to Bandura’s theory, there are four influences on self-efficacy, <b>Performance Accomplishments, Vicarious experience, Verbal persuasion, and Physiological state</b><ref name="bandura">Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191</ref>. Self-efficacy will affect people’s performance in every area of their life. Such as decision-making, problem-solving, and taking control in critical situations. The application of self-efficacy theory is widely used in education, business, and medicine to pursue higher achievement and better motivation. | ||
=='''Evidence'''== | =='''Evidence'''== | ||
In research on measuring teachers' self-efficacy(TSE), the four factors significantly impact TES development. This research uses Bandura's theory of self-efficacy to explain the pre-service teacher TSE development in their early practicum. Research predicts that vicarious experience and verbal persuasion will directly impact teachers' TSE. The research results show that all four factors can increase teachers’ self-efficacy( | [[File:Evidence table 6.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Both group teachers have increase of their TSE]] | ||
In research on measuring teachers' self-efficacy(TSE), the four factors significantly impact TES development. This research uses Bandura's theory of self-efficacy to explain the pre-service teacher TSE development in their early practicum. Research predicts that vicarious experience and verbal persuasion will directly impact teachers' TSE. The research results show that all four factors can increase teachers’ self-efficacy<ref name="Piz">Pfitzne-Eden, F.(2016), Why Do I Feel More Confident? Bandura's Sources Predict Preservice Teachers' Latent Changes in Teacher Self-Efficacy, Frontiers in Psychology, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01486/full</ref>, and students were most likely to be a source of verbal persuasion. Other sources of verbal persuasion were from school staff(e.g., social workers, teacher aides) and other preservice teachers (e.g., peers), which have a positive impact on teachers’ self-efficacy. Especially from a mentor teacher, verbal persuasion has a greater impact than an experienced, prestigious person. Additionally, mastery experience shows a strong connection to the changes in TSE. The more experienced teacher has, the better performance they get. In the early stage, the teacher gain confidence from the vicarious experience, but in the later stage, the impact of vicarious experience is decreasing. Considering the teachers are already received enough teaching experience, the decrease in the impact from vicarious experience is predictable. In the end, research shows evidence of lacking verbal persuasion and vicarious experience during teacher practicum have a negative impact on TSE. | |||
=='''Examples'''== | =='''Examples'''== | ||
Self-efficacy theory is widely used in K-12 curriculum design, classroom, and teacher's professional development. Through self-efficacy theory, it allows students to have the motivation to learn new knowledge and complete challenging task, maintain a stable mindset, and create a positive learning environment in K-12 setting. The application of self-efficacy can be cross-disciplinary and even outside the school. | Self-efficacy theory is widely used in K-12 curriculum design, classroom, and teacher's professional development. Through self-efficacy theory, it allows students to have the motivation to learn new knowledge and complete challenging task, maintain a stable mindset, and create a positive learning environment in K-12 setting. The application of self-efficacy can be cross-disciplinary and even outside the school. | ||
[[File:Fear to speak 1.png|200px|thumb|right|Fear of communicating with neighbors is a sign of lack of Performance Accomplishment. In the TV series, the man knocked on the door and left immediately, fearing to see the neighbors]] | |||
==='''Performance Accomplishment'''=== | |||
A positive experience is a powerful motivator to accomplish tasks. Previous success experiences will reinforce positive behavior and allow practice and skills improvement. The process will become a loop and increase overall performance<ref name="Lopze">Lopez-Garrido, G (2020). Self-efficacy. Simply Psychology.. https://www.simplypsychology.org/self-efficacy.html</ref>. The learner will acquire new skills in a low-pressure thinking environment. In the end, performance accomplishment can boost a person’s self-efficacy by thinking positively to believe they learn skills better. In curriculum design, when the teacher introduces a new topic, an experienced teacher will use scaffolding to help the student learn. With scaffolding, students can connect prior knowledge with new knowledge, which can gain some experience from the past. By using prior knowledge as a starter to start a new topic, with scaffolding, the student is learning new knowledge based on their previous"successful" experience. It is controllable for the teacher to motivate students to learn unfamiliar topics and complete challenging tasks. Conversely, learn without using scaffolding. Students will be less accepting of new knowledge, feel overwhelmed, and eventually lose motivation to learn. | |||
==='''Vicarious Experience'''=== | |||
By observing other people complete a task can also be a resource for increasing self-efficacy. One person’s behavior can influence others through the external environment as well as through the internal characteristics of the person<ref name="Martinez_motivation">Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ</ref>. If peers have done a challenging task successfully, a successful result from a peer can likely be an external factor influencing other people. Role models are everywhere in K-12 education, and teachers should always maintain and create role models for students to share vicarious experiences. A successful peer role model cannot only engage more students to learn better but is also beneficial for creating a positive collaborative learning environment. | |||
==='''Verbal Persuasion'''=== | |||
An energetic teacher can change the mood of a classroom. Conversely, a loud student can make classroom management difficult. Characteristics could be a factor that influences people’s behavior on tasks through social interaction. Similarly, verbal encouragement could also deliver a similar result to boost the motivation to accomplish specific tasks. Talking about self-esteem in education, encouraging students is common in school. The benefit of encouraging students will make students feel safe in the classroom. Teachers can also verbally show their respect and support to motivate their students. Verbal persuasion works at any age, but the earlier it is administered, the more it is likely to encourage the building of self-efficacy<ref name="Lopze">Lopez-Garrido, G (2020). Self-efficacy. Simply Psychology.. https://www.simplypsychology.org/self-efficacy.html</ref>. Relatively, if a teacher verbally criticizes a student, it may cause the student to feel frustrated and eventually stay away from the classroom. | |||
==='''Physiological State'''=== | |||
Emotional control and self-regulation are important skills both in school and outside of school. Having good self-regulation skills not makes you become a better student, and have better academic performance and learning motivation, but it could also make you become a strong, mature person. However, Bandura (1977) <ref name="bandura">Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191</ref>states, "it is not the sheer intensity of emotional and physical reactions that is important but rather how they are perceived and interpreted. People who have a high sense of efficacy are likely to view their state of affective arousal as an energizing facilitator of performance, whereas those who are beset by self-doubts regard their arousal as a debilitator. | |||
=='''Extension'''== | =='''Extension'''== | ||
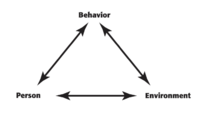
Limitation and Challenges | [[File:3mod.png|200px|thumb|right|Bandura's Triadic Reciprocality Model]] | ||
In Pfitzner's study on student-teacher practice, although the study provided a numerical model and designed a relatively reliable numerical data collection method, the researchers claimed that there were still many uncontrollable factors in the study. Such as teachers' previous knowledge, age, gender, personal experience, etc. These factors all affect the self-efficacy of the data. Although research can prove that self-efficacy can improve teachers' teaching efficiency in the early stage, it is difficult to further analyze the systemic influence. In the medical field, researchers have criticized Bandura's experiments on snake phobia in adults for ignoring the role of the environment and not referring to the impact of outcome expectations on self-efficacy ( | ==='''Limitation and Challenges'''=== | ||
In Pfitzner's study on student-teacher practice, although the study provided a numerical model and designed a relatively reliable numerical data collection method, the researchers claimed that there were still many uncontrollable factors in the study. Such as teachers' previous knowledge, age, gender, personal experience, etc. [[File:Harros-1997-Cycle-of-Socialization.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Cycle of Socialization]] These factors all affect the self-efficacy of the data. Although research can prove that self-efficacy can improve teachers' teaching efficiency in the early stage, it is difficult to further analyze the systemic influence. In the medical field, researchers have criticized Bandura's experiments on snake phobia in adults for ignoring the role of the environment and not referring to the impact of outcome expectations on self-efficacy <ref name="fez">Business Bliss Consultants FZE. (2018). Critical Analysis Of Self-Efficacy Theory. Retrieved from: https://nursinganswers.net/essays/critical-analysis-of-self-efficacy-theory-applied-nursing-nursing-essay.php?vref=1</ref>. | |||
Cycle of | ==='''Cycle of Socialization'''=== | ||
Bobbie Harro's Cycle of socialization is a model that explains the influence of the environment on the cognitive development of a person as grows up, and the influence of reinforcing social behavior in the interaction with people. | Bobbie Harro's Cycle of socialization is a model that explains the influence of the environment on the cognitive development of a person as grows up, and the influence of reinforcing social behavior in the interaction with people. | ||
=='''Reference'''== | =='''Reference'''== | ||
<references /> | |||
* | |||
<br> | |||
<div style="text-align: center;">'''Return to [[https://ectwiki.online/index.php?title=Motivation_Theory Motivation Theory]] | [[https://ectwiki.online/index.php?title=Main_Page Main Page]] | [[#top|[Top Page]]] '''</div> | |||
Latest revision as of 14:12, 16 December 2022
Overview[edit | edit source]
Psychologist Albert Bandura developed the self-efficacy theory in 1977. In psychology, self-efficacy is the belief that estimates people make about their ability to perform specific actions [1] . People are more likely to perform well in the field they are good at. The experience will gain confidence and lead the person to complete tasks. For example, professional basketball players will feel confident about any basketball-related activity. Still, they will feel less confident about an activity outside their skill pool, such as soccer. In Bandura’s theory, people with high self-efficacy usually believe they can perform well on specific tasks. But people with low self-efficacy are more likely to avoid complex tasks. The difference between high and low self-efficacy people reflects on their mindset on tasks and, more importantly, their understanding of external factors of the task. Based on knowledge of external factors will ultimately affect a person’s motivation to complete challenging tasks.
According to Bandura’s theory, there are four influences on self-efficacy, Performance Accomplishments, Vicarious experience, Verbal persuasion, and Physiological state[2]. Self-efficacy will affect people’s performance in every area of their life. Such as decision-making, problem-solving, and taking control in critical situations. The application of self-efficacy theory is widely used in education, business, and medicine to pursue higher achievement and better motivation.
Evidence[edit | edit source]
In research on measuring teachers' self-efficacy(TSE), the four factors significantly impact TES development. This research uses Bandura's theory of self-efficacy to explain the pre-service teacher TSE development in their early practicum. Research predicts that vicarious experience and verbal persuasion will directly impact teachers' TSE. The research results show that all four factors can increase teachers’ self-efficacy[3], and students were most likely to be a source of verbal persuasion. Other sources of verbal persuasion were from school staff(e.g., social workers, teacher aides) and other preservice teachers (e.g., peers), which have a positive impact on teachers’ self-efficacy. Especially from a mentor teacher, verbal persuasion has a greater impact than an experienced, prestigious person. Additionally, mastery experience shows a strong connection to the changes in TSE. The more experienced teacher has, the better performance they get. In the early stage, the teacher gain confidence from the vicarious experience, but in the later stage, the impact of vicarious experience is decreasing. Considering the teachers are already received enough teaching experience, the decrease in the impact from vicarious experience is predictable. In the end, research shows evidence of lacking verbal persuasion and vicarious experience during teacher practicum have a negative impact on TSE.
Examples[edit | edit source]
Self-efficacy theory is widely used in K-12 curriculum design, classroom, and teacher's professional development. Through self-efficacy theory, it allows students to have the motivation to learn new knowledge and complete challenging task, maintain a stable mindset, and create a positive learning environment in K-12 setting. The application of self-efficacy can be cross-disciplinary and even outside the school.
Performance Accomplishment[edit | edit source]
A positive experience is a powerful motivator to accomplish tasks. Previous success experiences will reinforce positive behavior and allow practice and skills improvement. The process will become a loop and increase overall performance[4]. The learner will acquire new skills in a low-pressure thinking environment. In the end, performance accomplishment can boost a person’s self-efficacy by thinking positively to believe they learn skills better. In curriculum design, when the teacher introduces a new topic, an experienced teacher will use scaffolding to help the student learn. With scaffolding, students can connect prior knowledge with new knowledge, which can gain some experience from the past. By using prior knowledge as a starter to start a new topic, with scaffolding, the student is learning new knowledge based on their previous"successful" experience. It is controllable for the teacher to motivate students to learn unfamiliar topics and complete challenging tasks. Conversely, learn without using scaffolding. Students will be less accepting of new knowledge, feel overwhelmed, and eventually lose motivation to learn.
Vicarious Experience[edit | edit source]
By observing other people complete a task can also be a resource for increasing self-efficacy. One person’s behavior can influence others through the external environment as well as through the internal characteristics of the person[1]. If peers have done a challenging task successfully, a successful result from a peer can likely be an external factor influencing other people. Role models are everywhere in K-12 education, and teachers should always maintain and create role models for students to share vicarious experiences. A successful peer role model cannot only engage more students to learn better but is also beneficial for creating a positive collaborative learning environment.
Verbal Persuasion[edit | edit source]
An energetic teacher can change the mood of a classroom. Conversely, a loud student can make classroom management difficult. Characteristics could be a factor that influences people’s behavior on tasks through social interaction. Similarly, verbal encouragement could also deliver a similar result to boost the motivation to accomplish specific tasks. Talking about self-esteem in education, encouraging students is common in school. The benefit of encouraging students will make students feel safe in the classroom. Teachers can also verbally show their respect and support to motivate their students. Verbal persuasion works at any age, but the earlier it is administered, the more it is likely to encourage the building of self-efficacy[4]. Relatively, if a teacher verbally criticizes a student, it may cause the student to feel frustrated and eventually stay away from the classroom.
Physiological State[edit | edit source]
Emotional control and self-regulation are important skills both in school and outside of school. Having good self-regulation skills not makes you become a better student, and have better academic performance and learning motivation, but it could also make you become a strong, mature person. However, Bandura (1977) [2]states, "it is not the sheer intensity of emotional and physical reactions that is important but rather how they are perceived and interpreted. People who have a high sense of efficacy are likely to view their state of affective arousal as an energizing facilitator of performance, whereas those who are beset by self-doubts regard their arousal as a debilitator.
Extension[edit | edit source]
Limitation and Challenges[edit | edit source]
In Pfitzner's study on student-teacher practice, although the study provided a numerical model and designed a relatively reliable numerical data collection method, the researchers claimed that there were still many uncontrollable factors in the study. Such as teachers' previous knowledge, age, gender, personal experience, etc.
These factors all affect the self-efficacy of the data. Although research can prove that self-efficacy can improve teachers' teaching efficiency in the early stage, it is difficult to further analyze the systemic influence. In the medical field, researchers have criticized Bandura's experiments on snake phobia in adults for ignoring the role of the environment and not referring to the impact of outcome expectations on self-efficacy [5].
Cycle of Socialization[edit | edit source]
Bobbie Harro's Cycle of socialization is a model that explains the influence of the environment on the cognitive development of a person as grows up, and the influence of reinforcing social behavior in the interaction with people.
Reference[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191
- ↑ Pfitzne-Eden, F.(2016), Why Do I Feel More Confident? Bandura's Sources Predict Preservice Teachers' Latent Changes in Teacher Self-Efficacy, Frontiers in Psychology, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01486/full
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lopez-Garrido, G (2020). Self-efficacy. Simply Psychology.. https://www.simplypsychology.org/self-efficacy.html
- ↑ Business Bliss Consultants FZE. (2018). Critical Analysis Of Self-Efficacy Theory. Retrieved from: https://nursinganswers.net/essays/critical-analysis-of-self-efficacy-theory-applied-nursing-nursing-essay.php?vref=1