Locus of control: Difference between revisions
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==='''External Locus of Control'''=== | ==='''External Locus of Control'''=== | ||
In an article from <i>Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication</i><ref name ="Shen_2017">Shen, L. (2017). Fatalism and Locus of Control as a Consideration When Designing Health and Risk Messages. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228613.013.341</ref>, having a level of external locus of control is normally associated with negative health conditions such as obesity, cancer, depression, to name a few. While research views external locus of control as negative<ref name="Shen_2017" />, an article from Verywell Mind<ref name="VerywellMind_2022">Are You in Control of Your Destiny, or Are You at the Mercy of Chance? (2022, October 17). Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-locus-of-control-2795434</ref> argues that having an external locus of control could possibly lower stress. | In an article from <i>Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication</i><ref name ="Shen_2017">Shen, L. (2017). Fatalism and Locus of Control as a Consideration When Designing Health and Risk Messages. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228613.013.341</ref>, having a level of external locus of control is normally associated with negative health conditions such as obesity, cancer, depression, to name a few. While research views external locus of control as negative<ref name="Shen_2017" />, an article from Verywell Mind<ref name="VerywellMind_2022">Are You in Control of Your Destiny, or Are You at the Mercy of Chance? (2022, October 17). Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-locus-of-control-2795434</ref> argues that having an external locus of control could possibly lower stress. This article uses a loss in a sports game as an example and explains that if the person applies external locus of control and pushes the responsibility to an unpleasant weather or a strong opposing team, the person may feel more stress free and less depressed<ref name ="VerywellMind_2022" />. | ||
==='''Characteristics'''=== | ==='''Characteristics'''=== | ||
Revision as of 22:20, 13 December 2022
Overview
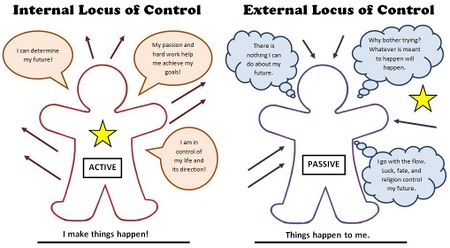
Based on Martinez[1], locus of control can be explained in two contrasting styles–internal locus of control and external locus of control. Internal locus of control refers to a person who thinks he/she has control over whatever happens to them–either good or bad. On the contrary, external locus of control refers to someone who believes he/she is being controlled by external forces and has no power over their circumstances.
Martinez[1] explains that internal locus of control is associated with the term ‘origin’, and external locus of control associates with the term ‘pawn’. Martinez further explains that those who are extremely passive about their lives are victims of what is called ‘learned helplessness’. Locus of control is important among the psychology community because it impacts our daily lives and influences our thoughts that may affect our actions[2].
Evidence
In a study related to health from CDC[3], a research was done for a group of youths of ages between 6 and 17 with chronic diseases to discover the relationship between locus of control and their health conditions. The results of the research discovered that a stronger internal LOC(locus of control) was associated with improved outcomes, and a stronger external LOC was linked to poorer outcomes[3]. This research also states an example of implementing a pain management program as a way to increase internal locus of control which allows patients to shift their beliefs toward feeling more in control of their own health condition.
This suggests that identifying the type of Locus of Control is highly valuable in regards to health care because knowing the outcomes of a type of locus of control may provide possible countermeasures for health care organizations that can be taken to improve health conditions of their patients.
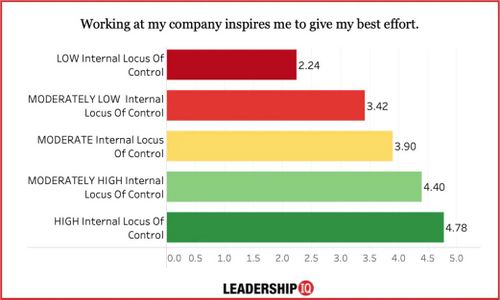
Internal Locus of Control
Research study shows that employees with higher internal locus of control are likely happy about their career and are likely to recommend their company to others. Based on the study, it also shows that employees are more likely to put much effort toward at work with higher internal locus of control[4]. Having a high internal locus of control suggests a better health condition, lower stress level, and greater confidence in self ability to influence outcomes[4]. To read the full article, visit here.
External Locus of Control
In an article from Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication[5], having a level of external locus of control is normally associated with negative health conditions such as obesity, cancer, depression, to name a few. While research views external locus of control as negative[5], an article from Verywell Mind[6] argues that having an external locus of control could possibly lower stress. This article uses a loss in a sports game as an example and explains that if the person applies external locus of control and pushes the responsibility to an unpleasant weather or a strong opposing team, the person may feel more stress free and less depressed[6].
Characteristics
[here]
Discover Your Locus of Control
[here]
Origin and Pawn
[here]
Example
[here]
Learned Helplessness
[here]
Evidence
Motivational Deficit
[here]
Cognitive Deficit
[here]
Emotional Deficit
[here]
Examples
[here]
Consequences and Treatment
[here]
Challenges and Further Consideration
[here]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ
- ↑ What Is Locus Of Control: And How It Affects Your Mind. (n.d.). Mind Help. https://mind.help/topic/locus-of-control/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Nazareth, M., Richards, J., Javalkar, K., Haberman, C., Zhong, Y., Rak, E., Jain, N., Ferris, M., & van Tilburg, M. A. (2016). Relating Health Locus of Control to Health Care Use, Adherence, and Transition Readiness Among Youths With Chronic Conditions, North Carolina, 2015. Preventing Chronic Disease, 13. https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd13.160046
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Api, S. (2022, March 11). Internal Locus Of Control: Definition And Research. Leadership IQ. https://www.leadershipiq.com/blogs/leadershipiq/internal-locus-of-control-definition-and-research
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Shen, L. (2017). Fatalism and Locus of Control as a Consideration When Designing Health and Risk Messages. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228613.013.341
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Are You in Control of Your Destiny, or Are You at the Mercy of Chance? (2022, October 17). Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-locus-of-control-2795434