Locus of control: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=='''Overview'''== | =='''Overview'''== | ||
[[File:9271000_orig.jpg|thumb|Internal and External Locus of Control|link=https://asinglebutterfly-scienceandela.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/2/3/19230179/9271000_orig.jpg]] | [[File:9271000_orig.jpg|450px|thumb|Internal and External Locus of Control|link=https://asinglebutterfly-scienceandela.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/2/3/19230179/9271000_orig.jpg]] | ||
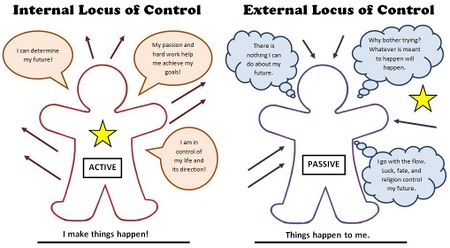
<p>Based on Martinez<ref name="Martinez">Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ</ref>, locus of control can be explained in two contrasting styles–<b>internal locus of control</b> and <b>external locus of control</b>. Internal locus of control refers to a person who thinks he/she has control over whatever happens to them–either good or bad. On the contrary, external locus of control refers to someone who believes he/she is being controlled by external forces and has no power over their circumstances.</p> | <p>Based on Martinez<ref name="Martinez">Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ</ref>, locus of control can be explained in two contrasting styles–<b>internal locus of control</b> and <b>external locus of control</b>. Internal locus of control refers to a person who thinks he/she has control over whatever happens to them–either good or bad. On the contrary, external locus of control refers to someone who believes he/she is being controlled by external forces and has no power over their circumstances.</p> | ||
<p>Martinez<ref name="Martinez" /> explains that internal locus of control is associated with the term ‘<b>origin</b>’, and external locus of control associates with the term ‘<b>pawn</b>’. Martinez further explains that those who are extremely passive about their lives are victims of what is called ‘<b>learned helplessness</b>’. Locus of control is important among the psychology community because it impacts our daily lives and influences our thoughts that may affect our actions<ref name="What_Is_Locus_of_Control">What Is Locus Of Control: And How It Affects Your Mind. (n.d.). Mind Help. https://mind.help/topic/locus-of-control/</ref>. | <p>Martinez<ref name="Martinez" /> explains that internal locus of control is associated with the term ‘<b>origin</b>’, and external locus of control associates with the term ‘<b>pawn</b>’. Martinez further explains that those who are extremely passive about their lives are victims of what is called ‘<b>learned helplessness</b>’. Locus of control is important among the psychology community because it impacts our daily lives and influences our thoughts that may affect our actions<ref name="What_Is_Locus_of_Control">What Is Locus Of Control: And How It Affects Your Mind. (n.d.). Mind Help. https://mind.help/topic/locus-of-control/</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 21:49, 13 December 2022
Overview
Based on Martinez[1], locus of control can be explained in two contrasting styles–internal locus of control and external locus of control. Internal locus of control refers to a person who thinks he/she has control over whatever happens to them–either good or bad. On the contrary, external locus of control refers to someone who believes he/she is being controlled by external forces and has no power over their circumstances.
Martinez[1] explains that internal locus of control is associated with the term ‘origin’, and external locus of control associates with the term ‘pawn’. Martinez further explains that those who are extremely passive about their lives are victims of what is called ‘learned helplessness’. Locus of control is important among the psychology community because it impacts our daily lives and influences our thoughts that may affect our actions[2].
Evidence
[here]
Internal Locus of Control
[here]
External Locus of Control
[here]
Characteristics
[here]
Discover Your Locus of Control
[here]
Origin and Pawn
[here]
Example
[here]
Learned Helplessness
[here]
Evidence
Motivational Deficit
[here]
Cognitive Deficit
[here]
Emotional Deficit
[here]
Examples
[here]
Consequences and Treatment
[here]
Challenges and Further Consideration
[here]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Martinez, M. E. (2010). Emotion, Motivation, and Volition. In Learning and Cognition: The Design of the Mind (pp. 153–188). Boston: Merrill. http://books.google.com/books?id=wqFWAAAAYAAJ
- ↑ What Is Locus Of Control: And How It Affects Your Mind. (n.d.). Mind Help. https://mind.help/topic/locus-of-control/