Experiential Learning: Difference between revisions
Tanvivartak (talk | contribs) |
Tanvivartak (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
According to Kolb's experiential learning model, there are four stages central to experiential learning. | According to Kolb's experiential learning model, there are four stages central to experiential learning. | ||
# '''Concrete Experimentation''' - | |||
# '''Collection of Data/ Reflective Observation -''' | |||
# '''Abstract Conceptualization''' | |||
# '''Active Experimentation''' | |||
= Example = | = Example = | ||
Revision as of 21:11, 23 February 2023
Overview
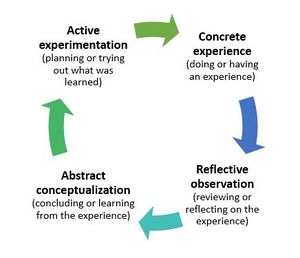
Experiential learning builds on the work of Piaget, Lewin and Dewey [1]. It consists of several models that stress the importance of direct experience and reflective observation
Kolb's Experiential Learning Model
According to Kolb's experiential learning model, there are four stages central to experiential learning.
- Concrete Experimentation -
- Collection of Data/ Reflective Observation -
- Abstract Conceptualization
- Active Experimentation
Example
Evidence
Implications and Design Critique
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Nielsen-Englyst, L. (2003). Game design for imaginative conceptualisation. Proceedings of the international workshop on experimantal interactive learning in industrial management, Allborg (pp. 149 – 164)